13
фев
13
фев
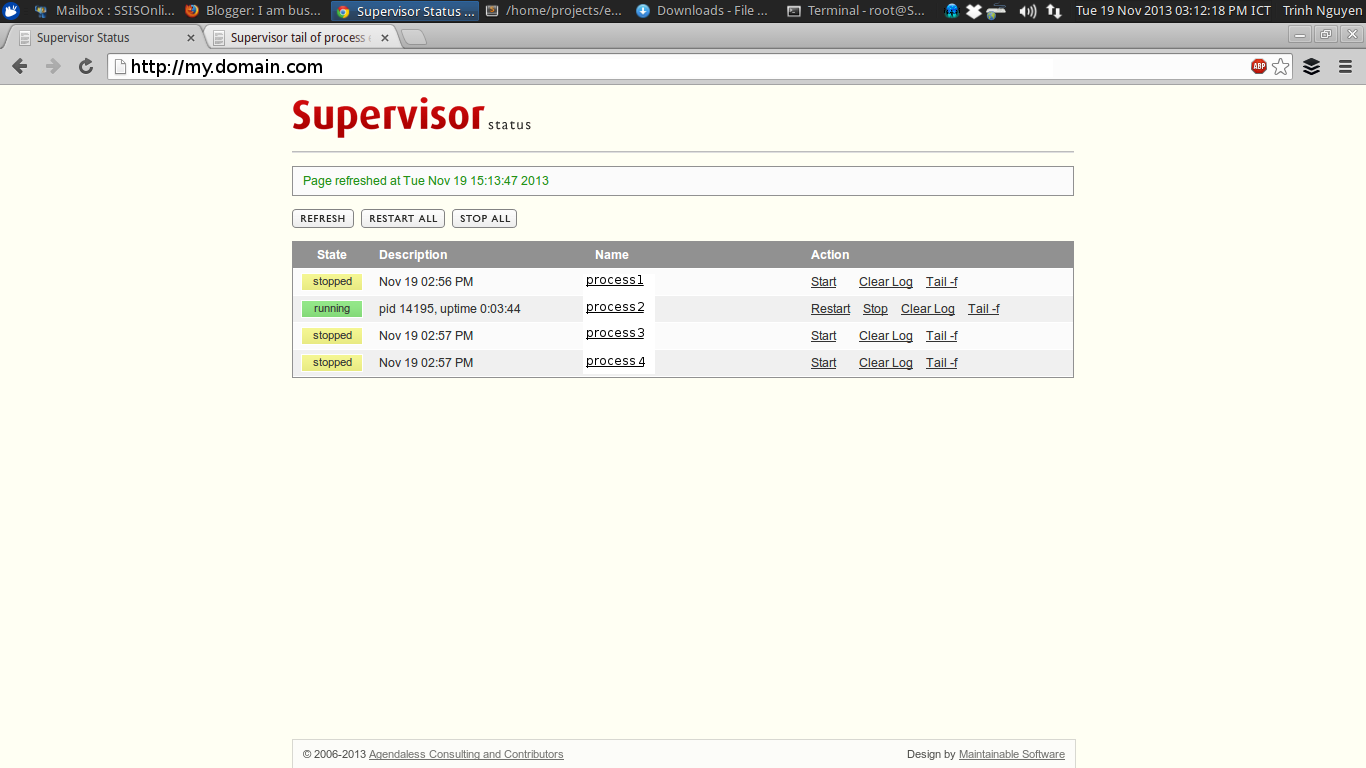
Feb 18, 2015 - supervisord in CentOS 7 (systemd version). Hello, Fast installation in CentOS 7 for this 'helper' to the queues service in laravel or django. (Last Updated On: September 10, 2018)Welcome to our guide on how to Install Netbox on CentOS 7 with Apache and Supervisord. NetBox is an open source web application designed to help manage and document computer networks. Initially conceived by the network engineering team at DigitalOcean. Netbox encompasses the following.
Preamble: Hi All, I’m a relatively inexperienced user, training to be a SA/DevOps guy who’s recently taken it upon himself to deploy the netbox db/app on Centos 6/7 respectively. While I’m aware that the deployment has been dockerized, and well documented on Debian based systems I thought I could learn something by taking the road less traveled. My goal with this document is to share some of the pitfalls I encountered while trying to adapt the installation to my process, in the hopes this can save others some time/effort in deploying the app under similar conditions. Installation parameters:. Centos 6 (referred to as host 1):.
PostgreSQL server.
KVM is an open source hardware virtualization software through which we can create and run multiple Linux based and windows based virtual machines simultaneously. KVM is known as Kernel based Virtual Machine because when we install KVM package then KVM module is loaded into the current kernel and turns our Linux machine into a hypervisor. In this post first we will demonstrate how we can install KVM hypervisor on CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x and then we will try to install virtual machines. Before proceeding KVM installation, let’s check whether your system’s CPU supports Hardware Virtualization. Run the beneath command from the console.
# grep -E '(vmx svm)' /proc/cpuinfo We should get the word either vmx or svm in the output, otherwise CPU doesn’t support virtualization. Jabra app android. Step:1 Install KVM and its associate packages Run the following yum command to install KVM and its associated packages.
Drivers magellan promark 3. # yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils Start and enable the libvirtd service # systemctl start libvirtd # systemctl enable libvirtd Run the beneath command to check whether KVM module is loaded or not # lsmod grep kvm kvmintel 162153 0 kvm 525409 1 kvmintel # In Case you have Minimal CentOS 7 and RHEL 7 installation, then virt-manger will not start for that you need to install x-window package. # yum install '@X Window System' xorg-x11-xauth xorg-x11-fonts-.
xorg-x11-utils -y Reboot the Server and then try to start virt manager. Step:2 Start the Virt Manager Virt Manager is a graphical tool through which we can install and manage virtual machines. To start the virt manager type the ‘ virt-manager‘ command from the terminal. # virt-manager Step:3 Configure Bridge Interface Before Start creating VMs, let’s first create the bridge interface.

Bridge interface is required if you want to access virtual machines from outside of your hypervisor network. # cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ network-scripts# cp ifcfg-eno49 ifcfg-br0 network-scripts# Edit the Interface file and set followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-eno49 TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=eno49 ONBOOT=yes BRIDGE=br0 Edit the Bridge file (ifcfg-br0) and set the followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-br0 TYPE=Bridge BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=br0 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.10.21 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.11 Replace the IP address and DNS server details as per your setup. Restart the network Service to enable the bridge interface.
# systemctl restart network # Check the Bridge interface using below command: # ip addr show br0 Step:4 Start Creating Virtual Machines. Now Create Virtual Machine either from the command line using ‘ virt-install‘ command or from GUI ( virt-manager ) Let’s Create a virtual machine of “ Windows Server 2012 R2” using virt-manager. Start the “virt-manager” Go to the File Option, click on “New Virtual Machine” We will be using ISO file as installation media. In the next step Specify the path of ISO file. Click on Forward. Specify the Compute Resources: RAM and CPU as per your setup. Click on Forward to proceed further.
Specify the storage Size of Virtual Machine, In my case I am using 25G. In the Next step Specify the Name of Virtual Machine and select network as ‘ Bridge bro’ Click on Finish to start the installation. Follow the screen instructions and complete the installation. Creating a virtual Machine from Command Line: Virtual Machines can be created from the console as well using ‘virt-install’ command. In the following example i going to virtual machine of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. # virt-install -name=Ubuntu-16-04 -file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu16-04.dsk -file-size=20 -nonsparse -graphics spice -vcpus=2 -ram=2048 -cdrom=ubuntu-16.04-server-amd64.iso -network bridge=br0 -os-type=linux -os-variant=generic Starting install. Allocating 'ubuntu16-04.dsk' 20 GB 00:00:00 Creating domain.
Follow the instruction now and complete the installation. In the above ‘virt-install’ command we have used following options:.
–name =. –file =. –file-size =.
–nonsparse =. –graphics =. –vcpu =. –ram =. –cdrom =.
–network =. –os-type =. –os-variant= Once the Installation is completed we can access the Virtual Machine console from ‘ virt-manager‘ as shown below.
That’s it, basic installation and configuration of KVM hypervisor is completed. This is awesome. I have been using it as my “gold standard” guide for getting VMs running on a CentOS 7 host. In fact, I don’t even use the GUI to get stuff going – I use the “Creating from a Command Line” as described above, then I do a “virsh console” to get the text console of the VM (as it boots from the install media), and do a “text” install (add “text” to the kernel/boot command line). No GUI ever used (just the way God intended Unix to be)! The only part that I thought was a bit confusing was the network and bridge setup.
The way it works is – the address info all gets set in the BRIDGE device – all your “real” device does is kind of “point” to the bridge.
Feb 18, 2015 - supervisord in CentOS 7 (systemd version). Hello, Fast installation in CentOS 7 for this 'helper' to the queues service in laravel or django. (Last Updated On: September 10, 2018)Welcome to our guide on how to Install Netbox on CentOS 7 with Apache and Supervisord. NetBox is an open source web application designed to help manage and document computer networks. Initially conceived by the network engineering team at DigitalOcean. Netbox encompasses the following.
Preamble: Hi All, I’m a relatively inexperienced user, training to be a SA/DevOps guy who’s recently taken it upon himself to deploy the netbox db/app on Centos 6/7 respectively. While I’m aware that the deployment has been dockerized, and well documented on Debian based systems I thought I could learn something by taking the road less traveled. My goal with this document is to share some of the pitfalls I encountered while trying to adapt the installation to my process, in the hopes this can save others some time/effort in deploying the app under similar conditions. Installation parameters:. Centos 6 (referred to as host 1):.
PostgreSQL server.
KVM is an open source hardware virtualization software through which we can create and run multiple Linux based and windows based virtual machines simultaneously. KVM is known as Kernel based Virtual Machine because when we install KVM package then KVM module is loaded into the current kernel and turns our Linux machine into a hypervisor. In this post first we will demonstrate how we can install KVM hypervisor on CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x and then we will try to install virtual machines. Before proceeding KVM installation, let’s check whether your system’s CPU supports Hardware Virtualization. Run the beneath command from the console.
# grep -E '(vmx svm)' /proc/cpuinfo We should get the word either vmx or svm in the output, otherwise CPU doesn’t support virtualization. Jabra app android. Step:1 Install KVM and its associate packages Run the following yum command to install KVM and its associated packages.
Drivers magellan promark 3. # yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils Start and enable the libvirtd service # systemctl start libvirtd # systemctl enable libvirtd Run the beneath command to check whether KVM module is loaded or not # lsmod grep kvm kvmintel 162153 0 kvm 525409 1 kvmintel # In Case you have Minimal CentOS 7 and RHEL 7 installation, then virt-manger will not start for that you need to install x-window package. # yum install '@X Window System' xorg-x11-xauth xorg-x11-fonts-.

xorg-x11-utils -y Reboot the Server and then try to start virt manager. Step:2 Start the Virt Manager Virt Manager is a graphical tool through which we can install and manage virtual machines. To start the virt manager type the ‘ virt-manager‘ command from the terminal. # virt-manager Step:3 Configure Bridge Interface Before Start creating VMs, let’s first create the bridge interface.

Bridge interface is required if you want to access virtual machines from outside of your hypervisor network. # cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ network-scripts# cp ifcfg-eno49 ifcfg-br0 network-scripts# Edit the Interface file and set followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-eno49 TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=eno49 ONBOOT=yes BRIDGE=br0 Edit the Bridge file (ifcfg-br0) and set the followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-br0 TYPE=Bridge BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=br0 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.10.21 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.11 Replace the IP address and DNS server details as per your setup. Restart the network Service to enable the bridge interface.
# systemctl restart network # Check the Bridge interface using below command: # ip addr show br0 Step:4 Start Creating Virtual Machines. Now Create Virtual Machine either from the command line using ‘ virt-install‘ command or from GUI ( virt-manager ) Let’s Create a virtual machine of “ Windows Server 2012 R2” using virt-manager. Start the “virt-manager” Go to the File Option, click on “New Virtual Machine” We will be using ISO file as installation media. In the next step Specify the path of ISO file. Click on Forward. Specify the Compute Resources: RAM and CPU as per your setup. Click on Forward to proceed further.
Specify the storage Size of Virtual Machine, In my case I am using 25G. In the Next step Specify the Name of Virtual Machine and select network as ‘ Bridge bro’ Click on Finish to start the installation. Follow the screen instructions and complete the installation. Creating a virtual Machine from Command Line: Virtual Machines can be created from the console as well using ‘virt-install’ command. In the following example i going to virtual machine of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. # virt-install -name=Ubuntu-16-04 -file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu16-04.dsk -file-size=20 -nonsparse -graphics spice -vcpus=2 -ram=2048 -cdrom=ubuntu-16.04-server-amd64.iso -network bridge=br0 -os-type=linux -os-variant=generic Starting install. Allocating 'ubuntu16-04.dsk' 20 GB 00:00:00 Creating domain.
Follow the instruction now and complete the installation. In the above ‘virt-install’ command we have used following options:.
–name =. –file =. –file-size =.
–nonsparse =. –graphics =. –vcpu =. –ram =. –cdrom =.
–network =. –os-type =. –os-variant= Once the Installation is completed we can access the Virtual Machine console from ‘ virt-manager‘ as shown below.
That’s it, basic installation and configuration of KVM hypervisor is completed. This is awesome. I have been using it as my “gold standard” guide for getting VMs running on a CentOS 7 host. In fact, I don’t even use the GUI to get stuff going – I use the “Creating from a Command Line” as described above, then I do a “virsh console” to get the text console of the VM (as it boots from the install media), and do a “text” install (add “text” to the kernel/boot command line). No GUI ever used (just the way God intended Unix to be)! The only part that I thought was a bit confusing was the network and bridge setup.
The way it works is – the address info all gets set in the BRIDGE device – all your “real” device does is kind of “point” to the bridge.
...">Install Supervisord Centos 7(13.02.2020)Feb 18, 2015 - supervisord in CentOS 7 (systemd version). Hello, Fast installation in CentOS 7 for this 'helper' to the queues service in laravel or django. (Last Updated On: September 10, 2018)Welcome to our guide on how to Install Netbox on CentOS 7 with Apache and Supervisord. NetBox is an open source web application designed to help manage and document computer networks. Initially conceived by the network engineering team at DigitalOcean. Netbox encompasses the following.
Preamble: Hi All, I’m a relatively inexperienced user, training to be a SA/DevOps guy who’s recently taken it upon himself to deploy the netbox db/app on Centos 6/7 respectively. While I’m aware that the deployment has been dockerized, and well documented on Debian based systems I thought I could learn something by taking the road less traveled. My goal with this document is to share some of the pitfalls I encountered while trying to adapt the installation to my process, in the hopes this can save others some time/effort in deploying the app under similar conditions. Installation parameters:. Centos 6 (referred to as host 1):.
PostgreSQL server.
KVM is an open source hardware virtualization software through which we can create and run multiple Linux based and windows based virtual machines simultaneously. KVM is known as Kernel based Virtual Machine because when we install KVM package then KVM module is loaded into the current kernel and turns our Linux machine into a hypervisor. In this post first we will demonstrate how we can install KVM hypervisor on CentOS 7.x and RHEL 7.x and then we will try to install virtual machines. Before proceeding KVM installation, let’s check whether your system’s CPU supports Hardware Virtualization. Run the beneath command from the console.
# grep -E '(vmx svm)' /proc/cpuinfo We should get the word either vmx or svm in the output, otherwise CPU doesn’t support virtualization. Jabra app android. Step:1 Install KVM and its associate packages Run the following yum command to install KVM and its associated packages.
Drivers magellan promark 3. # yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils Start and enable the libvirtd service # systemctl start libvirtd # systemctl enable libvirtd Run the beneath command to check whether KVM module is loaded or not # lsmod grep kvm kvmintel 162153 0 kvm 525409 1 kvmintel # In Case you have Minimal CentOS 7 and RHEL 7 installation, then virt-manger will not start for that you need to install x-window package. # yum install '@X Window System' xorg-x11-xauth xorg-x11-fonts-.

xorg-x11-utils -y Reboot the Server and then try to start virt manager. Step:2 Start the Virt Manager Virt Manager is a graphical tool through which we can install and manage virtual machines. To start the virt manager type the ‘ virt-manager‘ command from the terminal. # virt-manager Step:3 Configure Bridge Interface Before Start creating VMs, let’s first create the bridge interface.

Bridge interface is required if you want to access virtual machines from outside of your hypervisor network. # cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ network-scripts# cp ifcfg-eno49 ifcfg-br0 network-scripts# Edit the Interface file and set followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-eno49 TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=eno49 ONBOOT=yes BRIDGE=br0 Edit the Bridge file (ifcfg-br0) and set the followings: network-scripts# vi ifcfg-br0 TYPE=Bridge BOOTPROTO=static DEVICE=br0 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.10.21 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.10.1 DNS1=192.168.10.11 Replace the IP address and DNS server details as per your setup. Restart the network Service to enable the bridge interface.
# systemctl restart network # Check the Bridge interface using below command: # ip addr show br0 Step:4 Start Creating Virtual Machines. Now Create Virtual Machine either from the command line using ‘ virt-install‘ command or from GUI ( virt-manager ) Let’s Create a virtual machine of “ Windows Server 2012 R2” using virt-manager. Start the “virt-manager” Go to the File Option, click on “New Virtual Machine” We will be using ISO file as installation media. In the next step Specify the path of ISO file. Click on Forward. Specify the Compute Resources: RAM and CPU as per your setup. Click on Forward to proceed further.
Specify the storage Size of Virtual Machine, In my case I am using 25G. In the Next step Specify the Name of Virtual Machine and select network as ‘ Bridge bro’ Click on Finish to start the installation. Follow the screen instructions and complete the installation. Creating a virtual Machine from Command Line: Virtual Machines can be created from the console as well using ‘virt-install’ command. In the following example i going to virtual machine of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. # virt-install -name=Ubuntu-16-04 -file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu16-04.dsk -file-size=20 -nonsparse -graphics spice -vcpus=2 -ram=2048 -cdrom=ubuntu-16.04-server-amd64.iso -network bridge=br0 -os-type=linux -os-variant=generic Starting install. Allocating 'ubuntu16-04.dsk' 20 GB 00:00:00 Creating domain.
Follow the instruction now and complete the installation. In the above ‘virt-install’ command we have used following options:.
–name =. –file =. –file-size =.
–nonsparse =. –graphics =. –vcpu =. –ram =. –cdrom =.
–network =. –os-type =. –os-variant= Once the Installation is completed we can access the Virtual Machine console from ‘ virt-manager‘ as shown below.
That’s it, basic installation and configuration of KVM hypervisor is completed. This is awesome. I have been using it as my “gold standard” guide for getting VMs running on a CentOS 7 host. In fact, I don’t even use the GUI to get stuff going – I use the “Creating from a Command Line” as described above, then I do a “virsh console” to get the text console of the VM (as it boots from the install media), and do a “text” install (add “text” to the kernel/boot command line). No GUI ever used (just the way God intended Unix to be)! The only part that I thought was a bit confusing was the network and bridge setup.
The way it works is – the address info all gets set in the BRIDGE device – all your “real” device does is kind of “point” to the bridge.
...">Install Supervisord Centos 7(13.02.2020)